by James | Jan 18, 2023 | Welding
Welding is a process that involves the use of intense heat to join two pieces of metal together. One of the most important aspects of welding is the welding arc, which is the intense light and heat that is produced during the welding process. In this article, we will explore the brightness of a welding arc and how it is measured.
The heat and brightness of welding arcs can be unbelievably intense. The eyes are particularly vulnerable to arc damage, which is why welders must wear proper eye protection. The light from a welding arc might resemble the sun (especially at night).
What is a Welding Arc?
A welding arc is a type of electric arc that is formed between an electrode and the workpiece. The arc produces intense heat and light, which is used to melt the metal and join it together. The welding arc is an essential component of the welding process, as it provides the energy needed to melt the metal and create the weld.
How Bright is a Welding Arc?
The brightness of a welding arc is measured in units of luminous intensity, known as candela (cd). A typical welding arc can be as bright as 10,000 candela, which is about 50 to 100 times brighter than the sun. This intensity of light can cause damage to the eyes if proper protection is not worn. Here is the complete guide on how hot is a welder arc.
In comparison to the sun, how bright is a welding arc? No matter how intensely you perceive the welding arc, it is not brighter than the sun. There is a lot of heat generated by welding arcs as they are bright.
How Bright is a Welding Arc Compared to the Sun?
The brightness of a welding arc is typically measured in units of luminous intensity, known as candela (cd). A typical welding arc can be as bright as 10,000 candela, which is about 50 to 100 times brighter than the sun.
The sun has an intensity of about 100,000 candelas, so a welding arc is significantly brighter. This intense light can cause damage to the eyes if proper protection is not worn. That’s why it’s important to use the best welding helmet for eye protection while welding.
Factors that Affect Welding Arc Brightness
There are several factors that can affect the brightness of a welding arc, including:
- The type of welding process being used (e.g. TIG, MIG, Stick)
- The type of electrode being used
- The distance between the electrode and the workpiece
- The voltage and amperage of the welding machine
How to Measure Welding Arc Brightness
There are several ways to measure the brightness of a welding arc, including:
- Using a light meter
- Using a visual comparison chart
- Using a special instrument called a “welding arc viewer”
What is Welder Eye Or Arc Eye
Arc eye, also known as welder’s flash or flash burn, is a type of photokeratitis caused by exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from an electric arc. This condition causes inflammation and pain in the cornea and can lead to temporary vision loss. It is a common injury among welders.
But can also occur in people who are exposed to UV radiation in other ways, such as from tanning beds or from being close to a solar eclipse without proper eye protection. Wearing appropriate eye protection, such as a welding helmet with a filter lens, can help prevent arc eye.
What are the Types of Arc Welding Radiation?
There are three main types of radiation emitted during arc welding: ultraviolet (UV), visible light, and infrared (IR). Each type of radiation can have different effects on the eyes and skin, and it’s important to understand the risks associated with each one.
- Ultraviolet (UV) radiation: This type of radiation has the shortest wavelength and the highest energy of the three types. It is primarily responsible for causing arc eye, a condition that can lead to temporary vision loss.
- Visible light radiation: This type of radiation has a slightly longer wavelength and lower energy than UV radiation. It can cause glare and discomfort, but it is not as harmful as UV radiation.
- Infrared (IR) radiation: This type of radiation has the longest wavelength and the lowest energy of the three types. It can cause thermal burns to the skin and eyes, and can also cause glare and discomfort.
It’s important to note that all types of radiation emitted during arc welding can be harmful if the proper eye and skin protection are not worn. Wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as welding helmets, gloves, and protective clothing can help protect against these types of radiation.
Read More: What is Arc Blow in Welding
How to Protect Yourself From UV Damage Due to Welding?
Here are a few ways to protect yourself from UV damage while welding:
- Use appropriate eye protection: Always wear a welding helmet that has a filter lens that is specifically designed to block UV radiation. Make sure the helmet fits properly and that the lens is in good condition.
- Wear protective clothing: Long-sleeved shirts and pants, as well as gloves, can help protect your skin from UV radiation.
- Use appropriate ventilation: Welding in a well-ventilated area can help reduce your exposure to UV radiation.
- Take frequent breaks: Taking breaks every hour or so can help reduce your overall exposure to UV radiation.
- Keep a safe distance: The closer you are to the welding arc, the more intense the UV radiation will be. Try to keep a safe distance of at least 2 meters (6.5 feet) away from the arc whenever possible.
- Get Regular Eye Examinations: Regular eye check-ups will help you to detect any early signs of damage and to prevent further progression of the disease.
Conclusion
The welding arc is an essential component of the welding process, and its brightness is an important factor to consider. The brightness of a welding arc can be measured in candela and can range from 10,000 candela, which is very bright.
The brightness of the arc can be affected by several factors, including the type of welding process, the type of electrode, and the distance between the electrode and the workpiece. It’s important to use proper eye protection and measure the arc’s brightness to ensure the safety of the welder and those around them.
James is a welding expert, accomplished author, and trusted guide with over 8 years of experience in the industry. With his in-depth knowledge and engaging writing style, James has become a true authority in the field, offering readers and clients invaluable expertise and insights to take their welding skills to new heights.
by James | Jan 14, 2023 | Welding
Welding is a process that is used to join two metal parts together by heating them to a high temperature and then applying pressure to fuse them together. While welding can be a very effective way to join metal parts, it can also be a complex and challenging process that requires a high level of skill and experience to perform properly.
One of the most common challenges that welders face is arc blow, a phenomenon that can cause significant problems with the quality and consistency of the welds.
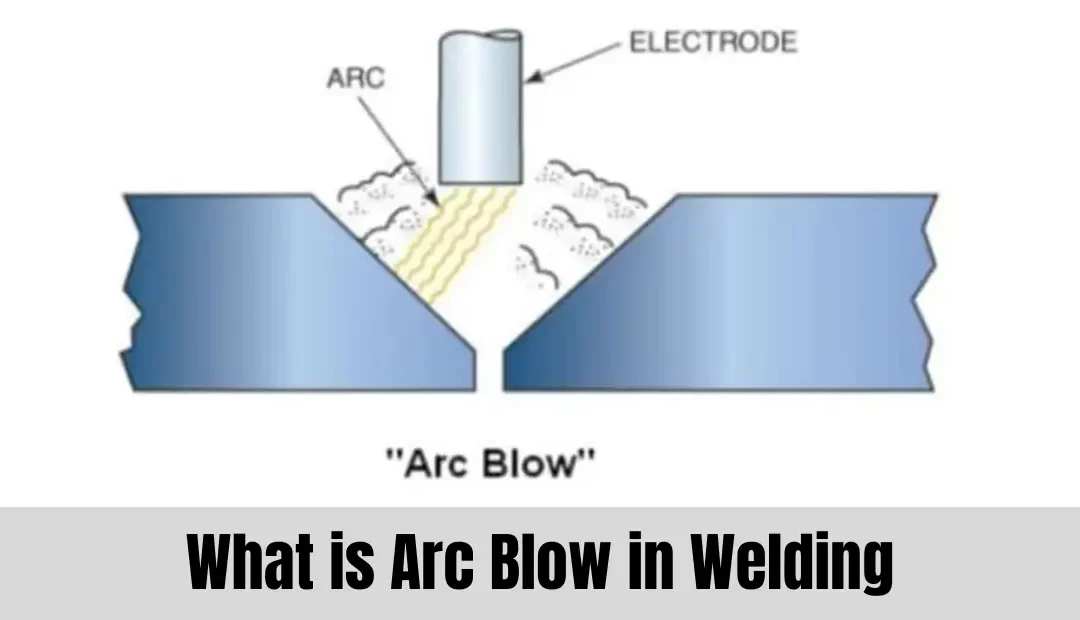
What is Arc Blow?
Arc blow is a phenomenon that occurs when an electric arc is used to weld metal parts together. It is caused by a magnetic field that is created around the welding arc. This magnetic field can cause the arc to be deflected and move in an unpredictable manner, making it difficult to control and resulting in poor-quality welds.
Arc blow is most commonly caused by a current imbalance between the two welding electrodes. This can occur when the welding electrodes are not properly aligned or when the welding machine is not set up correctly. The imbalance can also be caused by a number of other factors, such as the type of metal being welded, the thickness of the metal, and the position of the welding electrodes.
Symptoms of Arc Blow
Arc blow can be difficult to detect, but there are a few symptoms that can indicate that it is occurring. These include:
- A loud, humming or buzzing noise coming from the welding area
- A visible fluctuation in the welding arc
- A “wandering” arc that moves in an unpredictable manner
- Poor-quality welds that are uneven, porous, or have a rippled appearance
Read More: How to Prevent Welding Rod Sticking
What are the Types of Arc Blow Welding
Arc blow welding is a phenomenon that occurs during welding when the arc is deflected from its intended path, causing the weld to be of poor quality. There are several types of arc blow welding, including:
- Direct Current Arc Blow (DCAB): Direct Current Arc Blow occurs when using direct current (DC) welding power sources. The arc is deflected due to the presence of a magnetic field caused by the current flowing through the welding cable and workpiece.
- Alternating Current Arc Blow (ACAB): Alternating Current Arc Blow occurs when using alternating current (AC) welding power sources. The arc is deflected due to the changing direction of the current, which causes the magnetic field to fluctuate and push the arc in different directions.
- Low-Frequency Arc Blow (LFAB): Low-Frequency Arc Blow occurs when using low-frequency welding power sources. The arc is deflected due to the low-frequency oscillations of the current, which create a fluctuating magnetic field that pushes the arc in different directions.
- High-Frequency Arc Blow (HFAB): High-Frequency Arc Blow occurs when using high-frequency welding power sources. The arc is deflected due to the high-frequency oscillations of the current, which create a rapidly fluctuating magnetic field that pushes the arc in different directions.
- Electrode Negative Arc Blow (ENAB): Electrode Negative Arc Blow occurs when the electrode is connected to the negative terminal of the welding power source. The arc is deflected due to the magnetic field created by the current flowing through the electrode and workpiece.
- Electrode Positive Arc Blow (EPAB): Electrode Positive Arc Blow of arc blow occurs when the electrode is connected to the positive terminal of the welding power source. The arc is deflected due to the magnetic field created by the current flowing through the electrode and workpiece.
Arc blow welding can be prevented by using techniques such as adjusting the current and polarity, using a different type of welding power source, or by using a magnetic field correction device.
Read More: How Hot is an Arc Welder
Prevention and Correction
Preventing arc blow requires proper preparation and set up of the welding equipment and understanding the specific welding process and the metal being welded. Some of the ways that arc blow can be prevented include:
- Properly aligning the welding electrodes
- Using the correct welding machine settings
- Welding in the correct position
- Using the correct type of welding electrode
If an arc blow does occur, there are a few steps that can be taken to correct the problem. These include:
- Adjusting the welding machine settings
- Repositioning the welding electrodes
- Changing the type of welding electrode being used
- Changing the position of the welding electrodes
Conclusion
Arc blow is a common phenomenon that can occur when welding metal parts together. It is caused by a magnetic field that is created around the welding arc, which can cause the arc to move in an unpredictable manner, making it difficult to control and resulting in poor-quality welds. Arc blow can be prevented by proper preparation and set up of the welding equipment and understanding the specific welding process and the metal being welded.
If an arc blow does occur, there are steps that can be taken to correct the problem. By understanding the causes and symptoms of arc blow, welders can take steps to prevent it and ensure that their welds are of the highest quality.
Read More: What is a Flashback in Welding
James is a welding expert, accomplished author, and trusted guide with over 8 years of experience in the industry. With his in-depth knowledge and engaging writing style, James has become a true authority in the field, offering readers and clients invaluable expertise and insights to take their welding skills to new heights.

by James | Jan 7, 2023 | Welding
MIG welding, also known as gas metal arc welding (GMAW), is a common welding process that is widely used in various industries. It is a popular choice because there are many advantages of MIG welding, including its versatility, high speed and ease of use. MIG welding is a process in which an electrode is used to create an electric arc between the base metal and the wire, which melts and fuses the metal together.
MIG welding is known for its high speed and ability to produce strong, high-quality welds. It is easy to use and produces clean welds. In addition, it is fast and has higher productivity than other methods. In this article, we will explore the various advantages of MIG welding in detail.
Read More: Best Welding Helmets for MIG Welding
MIG Welding has Higher Productivity
When looking for ways to increase productivity, many people look to MIG welding. This welding technique produces high-quality welds while providing a higher rate of deposition. Compared to TIG welding, MIG is faster and easier to learn. This can save time and money in the long run. It is also suitable for thinner materials.
Unlike TIG welding, it is used on a variety of metals, including aluminum. The process uses a continuous wire feed, which allows for better penetration and welding control. Aside from speed, this process also produces a stronger, more reliable weld.
The most common reactive gas used in MIG welding is carbon dioxide. This is cheaper than other gases but has disadvantages like more spatter. For thicker materials, helium is a viable alternative. It has 10 times the thermal conductivity of argon, but it is limited to applications where the joint is too thick to be welded entirely.
Read More: How to Weld Cast Iron
It is Simple and Great Welds
Using MIG Welding is simple and great welds are achievable. However, learning how to weld requires a lot of practice. Before you start welding, clean the surface. This is necessary for safety reasons. You can use a metal brush to remove rust and mill scale.
In addition, wear appropriate safety gear. Always make sure to check your gas hose for leaks. If you find one, get a new hose. Next, learn about different weld patterns. Choosing the right technique can improve the quality of your final weld. For example, a push-pull weld method provides better visibility of your work.
When you learn how to MIG weld, it’s important to keep a close eye on your weld puddle. If you notice the weld puddle isn’t centered, you’ll need to adjust your travel speed.
MIG Welding is Clean and Efficient
MIG welding is an efficient and clean way to weld a variety of metals. It is suitable for a wide range of metals, including iron, aluminum, steel, and magnesium. Unlike TIG welding, MIG welds do not produce a lot of spatters and require little finishing. This makes it a good choice for welds that will be applied in closed and clean environments.
Before you buy a MIG welder, it’s important to know what the equipment can and can’t do. For example, MIG welders cannot be used overhead. Also, they aren’t suitable for wet and windy conditions. They also require gas lines, which can get in the way when welding.
MIG welders use a mixture of argon and carbon dioxide to form an arc between the wire and the base metal. The shielding gas protects the weld pool from impurities.
Read More: Best Shade Lens for MIG Welding
Long-Pass Welding
Long-pass welding is a type of welding process that involves making a series of overlapping passes along the length of the weld joint in order to build up the weld bead. This process is typically used for welding thick materials or for making repairs to damaged welds. It is a slower process than some other welding methods, but it can produce strong, high-quality welds.
Some of the main advantages of long-pass welding include its ability to produce strong welds, its versatility, and its ability to accommodate a variety of materials and thicknesses. However, it can also be more time-consuming and require more skill to perform than some other welding processes.
MIG Welding is Versatile
MIG welding is one of the most versatile types of welding processes. It can be used on all kinds of metals. The process has a cleaner appearance and is much faster than other welding methods. MIG is a semi-automatic, gas metal arc welding process.
MIG welders use a wire electrode that is supplied on a spool. Using this wire, the welder continuously feeds shielding gas into the weld pool. This shielding gas protects the weld area from atmospheric gases. Shielding gas can be either inert or reactive. Both gasses can be pumped into the weld pool.
Inert gases are beneficial in that they protect the weld from oxygen and other contaminants. Depending on the type of metal being welded, different gasses are required. For higher precision, TIG welding is preferred. However, it is more costly than MIG and does not produce as precise welds.
Read More: What is Cold Welding
It has a Faster Welding Speed
MIG welding is a semi-automatic welding process that uses consumable electrodes. The electrodes are shaped to the size and composition of the metal. This helps to create an electric arc that melts the base material.
In addition to consumable electrodes, MIG welding requires the use of shielding gas. Shielding gas protects the welded area by preventing contaminants from entering the weld pool. Other gases can also be used for this purpose.
The arc created by MIG welding is a more stable one than that of stick welding. It also produces less weld spatter and less slag. Another advantage of MIG welding is its ability to weld thin metals and large parts. This means that it can handle higher production runs. Also, MIG welding does not need brushing and chipping away of slag.
Final Words – Advantages of MIG Welding
MIG welding has many advantages that make it a popular choice among welders. Some of the main advantages of MIG welding include its versatility, high speed, and ease of use. MIG welding can be used on a wide range of materials, including steel, aluminum, and stainless steel, and it is suitable for both thick and thin materials.
It is also a fast welding process, which means that it can be used to complete projects quickly and efficiently. Additionally, MIG welding is relatively easy to learn, making it a good choice for beginners or those who are new to welding. Overall, MIG welding is a reliable and efficient welding process that is well-suited for a variety of applications.
Read More: Is Welding a Good Career
James is a welding expert, accomplished author, and trusted guide with over 8 years of experience in the industry. With his in-depth knowledge and engaging writing style, James has become a true authority in the field, offering readers and clients invaluable expertise and insights to take their welding skills to new heights.

by James | Jan 1, 2023 | Welding
It is possible to weld pot metal, die-cast aluminum or zinc alloy. However, it can be challenging because pot metal has a low melting point and is prone to cracking and warping. Additionally, it is often contaminated with other metals or impurities, making the welding process more difficult.
To weld pot metal, you must use a low-temperature welding process such as brazing or soldering. These methods use a filler metal with a lower melting point than the pot metal, which allows you to join the pieces without melting the base metal. You will also need to use flux, a chemical agent that helps remove impurities and improve the filler metal flow.
It is important to prepare the pot metal surfaces carefully before welding. It also involves cleaning the metal to remove any dirt, oil or other contaminants and shaping or filing the edges to create a clean, smooth surface for the filler metal.
Welding pot metal can be challenging and requires a skilled hand and careful attention to detail. If you are not experienced in welding, it may be best to seek the help of a professional. Here is also a guide on how to weld cast iron.
If you are looking to weld some pot metal, there are a few things you will need to know:
- You need to identify the type of pot metal you will weld.
- You need to find out how to weld it.
- You will need to be aware of the safety considerations.
How To Identify Pot Metal
Pot metal is a mixture of several metals, such as zinc, aluminum, and lead. It is a cheap metal alloy. In the past, pot metal was used for various objects in homes, auto repair shops, and factories. Today, it is also used in plastics.
Pot metal has low melting points, which makes it easy to cast. However, this process can be dangerous. The metal is susceptible to cracking and breaking. If the pot metal is not of high quality, the casting process may end up with an unusable part.
Pot metal was originally used in automobile factories during the early 20th century. It was produced by melting scrap metals into a pot. This way, it could be reused and recast in factories. Another use of pot metal was in jewelry.
Read More: What is Undercut Welding?
What is Pot Welding
Pot welding is a process that uses a metal that has a low melting point. This type of metal can be made from zinc, tin, aluminum, or lead. Some of these alloys can be difficult to weld. This method is used in many industries. For instance, it is used in the automotive industry. It is also widely used in the aerospace industry.
In pot welding, a welding electrode applies pressure to a workpiece. The resulting weld is formed by fusion. However, when too much pressure is applied, the weld can crack or the resulting joint may be weakened.
A weld is formed when a metal is fused using a large amount of energy in a short time. When welding, the amount of electric current applied to the metal will depend on the thickness of the metal.
Can Pot Metal be Welded
Pot metal, also known as monkey metal or die-cast zinc, is a mixture of minerals with a low melting point. It is often used for cheap castings. However, it isn’t easy to weld. Pot metal is often found in the auto repair industry. It is because the metal is relatively inexpensive. But its unique qualities make it difficult to work with it.
Pot metal is a mixture of low-melting-point metals, which makes it very challenging to weld. For this reason, it is best to use TIG welding. Also, you need to prepare the parts properly before the welding process. You should clean them well to remove any dirt and corrosion.
When you are ready to start the welding, you should apply SI Structural Adhesive to both sides of the pot metal. Make sure the adhesive dries before you proceed with the rest of the weld.
Read More: What is Cold Welding?
Things To Know Before Welding Pot Metal
Pot metal welding is not a trivial task. It requires time, skill and talent. If you can weld pot metal, you will enjoy the satisfaction of preserving your scrap metal.
First, identify the type of pot metal. Different types have different physical properties. Some can be difficult to weld and repair. You can tell if a part is pot metal by weighing it or using magnets. Next, you’ll need to choose the correct equipment for the job. TIG welding is the most effective method for welding pot metal.
The best equipment is an A/C tig welder with a high-frequency start because it provides a strong arc. Once the metal is hot, you’ll want to apply liquid flux. It is a mixture of different elements that can help the joint melt.
How to Weld Pot Metal
Whether you’re welding pot metal for a project or a hobby, it’s important to follow some basic steps to get the best results. Although it’s not as simple as traditional welding, it’s also one of the most effective ways to preserve scrap metal.
Welding pot metal isn’t a very difficult process, but it does take a certain amount of time and expertise. It would help if you started by making some test pieces of pot metal. Then, use these to practice. Before you try your skills on a real item, ensure you have all the necessary equipment.
Using a tig welder is a great way to weld pot metal. It’s likely more convenient than other welding methods. But tig welding requires experience and knowledge of aluminum welding.
Read More: What is Arc Welding?
Can You Solder Pot Metal?
Yes, it is possible to solder pot metal, also known as die-cast aluminum or zinc alloy. However, it can be challenging because pot metal has a low melting point and is prone to cracking and warping. Additionally, it is often contaminated with other metals or impurities, making the soldering process more difficult.
To solder pot metal, you will need to use a low-temperature soldering process. It may involve using a soldering iron with a lower temperature setting or a soldering wire with a lower melting point than the pot metal. You will also need to use flux, a chemical agent that helps remove impurities and improve the flow of the solder.
It is important to carefully prepare the pot metal surfaces before soldering. It may involve cleaning the metal to remove any dirt, oil, or other contaminants and shaping or filing the edges to create a smooth surface for the solder to bond.
Soldering pot metal can be challenging and requires a skilled hand and careful attention to detail. If you are not experienced in soldering, seek the help of a professional.
Read More: What is a Flashback in Welding?
How to Weld Broken Pot Metal?
To weld broken pot metal, you will need to use a special type of filler called “pot metal filler.” It is because pot metal is a low-quality alloy that is prone to cracking and unsuitable for welding with traditional filler metals.
To weld pot metal, clean the area to be repaired with a wire brush to remove any dirt or debris. Next, preheat the pot metal to about 200-300 degrees Fahrenheit. Then, apply the pot metal filler to the area using a MIG welder, carefully following the manufacturer’s instructions. Finally, allow the repair to cool before handling the object.
Read More: How to Prevent Welding Rod Sticking
James is a welding expert, accomplished author, and trusted guide with over 8 years of experience in the industry. With his in-depth knowledge and engaging writing style, James has become a true authority in the field, offering readers and clients invaluable expertise and insights to take their welding skills to new heights.

by James | Dec 25, 2022 | Welding
When you are trying to weld the metal, there are several ways to prevent a welding rod sticking to the base metal. One of the best ways to avoid this problem is to keep the rod’s tip free of the base metal.
Make sure to clean the metal surface before welding to remove any dirt, debris, or rust. It will help to ensure a good weld. Also, check the differences between a good weld and bad weld.
Use a flux-coated rod because it has a chemical substance that helps to prevent the rod from sticking to the metal. Make sure to use the correct welding technique for the type of metal and welding process.
Use backing strip or backing bar pieces of metal placed behind the weld joint to support the molten metal as it cools and solidifies. It can help to prevent the welding rod from sticking to the metal.
Best Way to Strike an Arc
Here are simple tips and techniques to strike an Arc to prevent the welding rod from sticking to the metal. These tips will help you make the most of your arc and save time.
First, make sure that the metal is grounded properly. You may have difficulty striking the arc if the ground is not connected properly. Another problem is if the wire is cracking. It can interfere with the electric flow.
Next, set your welder’s parameters. Using the correct arc length for the type of metal you are working with is important. For example, if you are welding stainless steel, you should use a lower amperage setting than welding copper.
Finally, strike the arc on a piece of steel at least 3 inches across. Practice using an arc until you get the hang of it. To strike the arc, start by holding the electrode at an angle. Hold it about an inch above the starting point.
Reasons Why Welding Rod Stick to the Base Metal
You may notice that your welding rod sticks to the base metal when welding. It can be a very frustrating experience. The good news is that the sticking is not permanent and can be easily fixed.
Welding rods stick to the base metal for a variety of reasons. Regardless of the cause, it’s important to understand how to fix the problem. First, make sure that your electrodes are not degraded. Poor-quality electrodes will stick to the workpiece.
Also, it would help if you stored your electrodes correctly. Usually, electrodes need to be stored in a dry, cool place. If your electrodes are stuck to the workpiece, you can use a chipping hammer to loosen them. Second, make sure that you are using the correct arc length.
An arc length is a distance between the electrode and the base metal. An arc that is too long will leave your electrodes hot and will not allow the flux to perform well. Finally, ensure that you are holding your welding rod at the correct angle. Normally, electrodes are held at an angle of 20 to 30 degrees.
Tips to Avoid Welding Rod Sticking to the Metal
It is important to understand how to avoid welding rods sticking to the metal when stick welding. It is a common rookie mistake, but with some precautions, you can keep your welds looking great.
The first step is to clean up any rust or moisture in the welding area. These areas will hinder the electric flow and cause problems.
Secondly, you must maintain proper joint geometry. Without proper joint geometry, the electrode will have difficulty reaching the joint.
Thirdly, you should maintain a small arc length. Keeping the arc length short will help prevent arcing-in.
Fourthly, it would help if you always used good-quality electrodes. A poor-quality electrode will tend to get stuck to the metal.
Finally, it would be best if you perfectly stored your welding electrodes. If you use E7018 or E7024 electrodes, you do not need to worry about special storage. They can be stored in dry ovens at 200-400 degrees Fahrenheit.
It is also important to practice with your welding equipment. You can avoid material waste and save time by learning how to strike an arc.
How to Fix the Tip of a Stuck Welding Rod?
Welding rods get stuck to the metal and can ruin a good-looking weld. There are several ways to fix the tip of a stuck welding rod. However, remember that a good weld is only made if the electrodes are set properly.
The most common reason for rod sticking is low amperage values. When your amperage is too low, you cannot strike an arc.
Another common cause of rod sticking is the wrong size of electrodes. If unsure about your electrode sizes, you can look for a chart.
Besides that, a stuck welding rod can also be caused by improper storage. To avoid such a situation, you should store your electrodes in a dry and cool place.
Try jerking your welding rod to free it. It is best to use a pair of thick, dry welding gloves. It will help keep your hands safe while you are removing the rod.
It is important to avoid jerking the rod because this can break the flux around the rod’s tip. Once you break the bond, the flux will fall off the rod and stick to the metal.
What to Do When Welding Rod Gets Stuck with Metal?
When a welding rod gets stuck to the metal, it can be a big problem. It can lead to a poor-looking weld and cause a faulty arc. There are many things to check when you are experiencing this problem. This article will discuss a few of the most common causes and tips to help you get the rod back in working order.
One of the most obvious reasons for welding rod sticking is the wrong electrode size. The electrode should be sized properly according to the type of weld you are making. Another reason for sticking is an inadequate amperage value. A low amperage value can lead to incorrect welding techniques and cause a weld to stick.
If you’re unsure of the best amperage for your welding application, consult an electrode chart. These charts are available online. When using a stick welder, you should always try to keep your arc length to a minimum. Keeping your arc short will prevent arcing-in.
Keep Your Amperage High
Suppose you are struggling with a welding rod that keeps sticking to the metal. Follow this tip that will help you to solve the problem. It is important to keep your amperage high to avoid the stick welding issue.
To get a clean weld, you must ensure that you are welding at the correct speed and angle. Also, you need to ensure that your base metal is clean. You should also wear thick gloves. The most common cause of a welding rod sticking to the metal is a low amperage value.
It is because a low amperage is not sufficient for the arc to strike. Moreover, it can cause a stuttering arc or even an arc that will fade away. Another reason a welding rod might stick is the resistance caused by the base metal.
Rust and dust increase the resistance. Moreover, a painted surface can hinder the electric flow. One of the best ways to fix a welding rod sticking to the metal is to remove the flux. Removing the flux will give you a clean connection to the weld.
Don’t Use a Hot Rod
A welding rod that sticks to metal can ruin a perfectly executed weld. It can be frustrating, but there are steps you can take to help prevent it. To start, you should wear good-quality gloves. It will protect your hands from getting burned.
It would be best if you also were careful when removing a rod. You may lose the arc if you try to pull a rod off too far. When ready to strike the arc, you should tilt the rod in the direction of the weld. Make sure the rod is one inch above the base metal. The rod will create a crater as it moves over the joint.
One of the best ways to prevent your rod from sticking to the base metal is to use a high-quality rod. Some rods can be very hot when you strike the arc. Another way to help keep your rod from sticking is to use a cut-off grinder. It will help remove the flux around the tip of the rod.
Pulling an Electrode from a Work Piece
A welding rod can stick to the metal on which it is used. Several factors usually cause this. Some include incorrect electrode size, poor electrode handling, and uneven flux. It can also be a result of a low amperage value.
Fortunately, it is possible to prevent your welding rod from sticking from your workpiece if necessary. The first step is to ensure your electrode is properly stored. It should not be rusty or degraded.
It would help if you also had an adequate pair of dry and thick gloves to protect your hands. Your electrode needs to be held at an angle of between 20 to 30 degrees. Holding your electrode at too steep an angle can cause the electrode to stick to the metal.
In addition, holding your electrode at too shallow an angle can cause a poor-looking weld. Another factor to consider is the length of your arc. The longer the arc, the more heat it will lose. If the arc length is too long, it may cause splatter.
Conclusion
There are several ways to prevent welding rods from sticking to the metal when welding. The best approach is to follow proper welding techniques and use a combination of methods, such as cleaning the metal surface.
You can also use a backing strip or bar, a flux-coated rod or remove any stuck welding rod with a wire brush or grinding wheel. Following these steps can ensure a successful and smooth welding process.
James is a welding expert, accomplished author, and trusted guide with over 8 years of experience in the industry. With his in-depth knowledge and engaging writing style, James has become a true authority in the field, offering readers and clients invaluable expertise and insights to take their welding skills to new heights.






