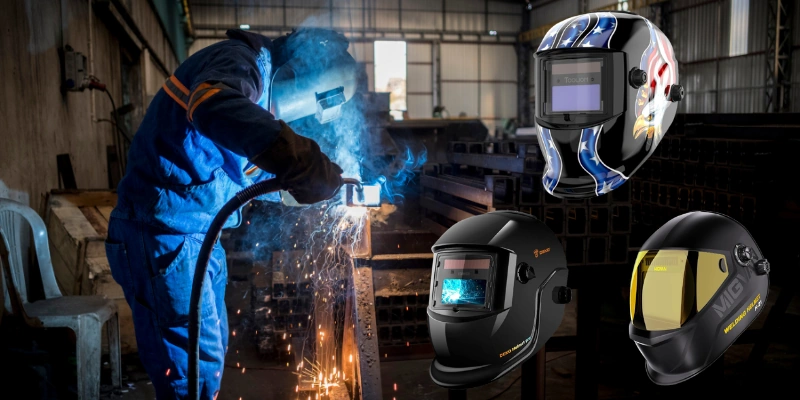
Welding is a crucial process in manufacturing and construction, requiring both skill and the right equipment. One of the most important specifications when choosing a welding machine is its duty cycle. But what exactly is the duty cycle in welding, and why is it so important? This article will delve deep into the concept of the duty cycle, its significance, and how it affects your welding projects.
Table of Contents
Understanding Duty Cycle in Welding
The duty cycle in welding refers to the percentage of time a welding machine can operate continuously within 10 minutes before it cools down. It’s typically expressed as a percentage at a specific amperage output.
How Duty Cycle Works
For example, if a welder has a 60% duty cycle at 300 amps, it means:
- The machine can weld continuously for 6 minutes (60% of 10 minutes) at 300 amps
- It then needs to cool down for 4 minutes before starting another welding cycle
Why Duty Cycle Matters in Welding
- Prevents Overheating: The duty cycle helps prevent the welding machine from overheating, which can damage internal components.
- Ensures Consistent Weld Quality: Operating within the specified duty cycle ensures consistent weld quality throughout your project.
- Impacts Productivity: A higher duty cycle allows for longer continuous welding times, potentially increasing productivity.
- Affects Machine Selection: Understanding the duty cycle helps choose the right welding machine for your specific needs.
Factors Affecting Duty Cycle
Several factors can influence a welding machine’s duty cycle:
- Amperage Output: Generally, as the amperage increases, the duty cycle decreases.
- Ambient Temperature: Higher ambient temperatures can reduce the effective duty cycle.
- Machine Design: Industrial-grade welders typically have higher duty cycles than hobbyist models.
- Welding Process: Different welding processes (MIG, TIG, Stick) can have varying effects on duty cycle.
How to Calculate Duty Cycle
To calculate the duty cycle, use this formula:
Duty Cycle = (Weld Time / Total Cycle Time) x 100For example, if you weld for 3 minutes out of a 10-minute cycle:
(3 minutes / 10 minutes) x 100 = 30% duty cycleTips for Managing Duty Cycle
- Choose the Right Machine: Select a welding machine with a duty cycle appropriate for your projects.
- Monitor Welding Time: Keep track of your continuous welding time to avoid exceeding the duty cycle.
- Adjust Amperage: Lower amperage settings often allow for longer duty cycles.
- Plan Your Work: Organize your welding tasks to allow for cooling periods.
- Improve Ventilation: Good airflow around the welding machine can help maintain its duty cycle.
Conclusion
Understanding the duty cycle is crucial for both professional welders and hobbyists. It affects the quality of your welds, the longevity of your equipment, and your overall productivity. By considering the duty cycle when selecting and using welding equipment, you can ensure better results and a more efficient welding process.
Remember, while a higher duty cycle can be beneficial, it’s essential to choose a welding machine that matches your specific needs and budget. Always consult the manufacturer’s specifications and guidelines to make the most of your welding equipment.

James is a welding expert, accomplished author, and trusted guide with over 8 years of experience in the industry. With his in-depth knowledge and engaging writing style, James has become a true authority in the field, offering readers and clients invaluable expertise and insights to take their welding skills to new heights.