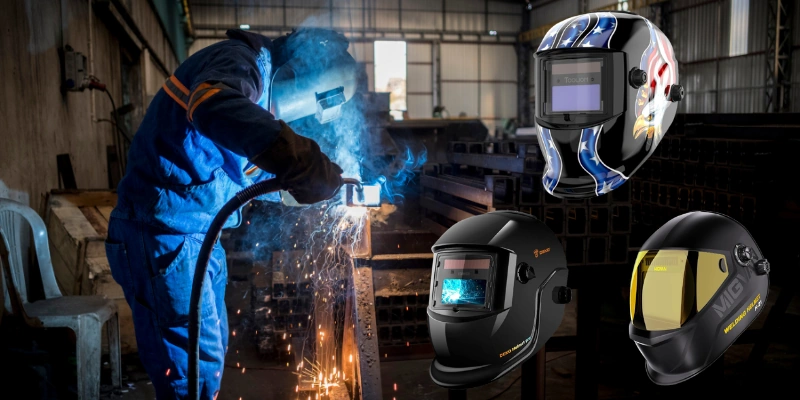
Welding is a crucial process in various industries, from construction to automotive manufacturing. Among the many welding techniques, tack welding plays a vital role in ensuring the stability and accuracy of final welds. Also check the differences between tack welding and spot welding. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into what tack welding is, the role of a tack welder, and the essential skills and equipment needed for the job.
Table of Contents
What is Tack Welding?
Tack welding is a temporary welding process used to hold pieces of metal together in preparation for final welding. It involves making small, temporary welds—called tack welds—at strategic points along the workpieces. These tack welds serve to align and stabilize the parts, preventing movement and distortion during the final welding process.
Key Features of Tack Welding
- Temporary Joints: Tack welds are not meant to withstand significant loads or stresses. They are temporary and often removed or incorporated into the final weld.
- Precision Alignment: Tack welds ensure that the workpieces are precisely aligned and held in the correct position.
- Distortion Prevention: By stabilizing the parts, tack welds help prevent warping or shifting during the final welding.
The Role of a Tack Welder
A tack welder specializes in creating these temporary welds to set up the workpieces for the final welding process. The role of a tack welder is crucial in ensuring the quality and accuracy of the final welds.
Responsibilities of a Tack Welder
- Preparation: Cleaning and preparing the surfaces to be welded.
- Alignment: Precisely aligning the workpieces according to blueprints and specifications.
- Tack Welding: Applying tack welds at strategic points to hold the pieces together.
- Inspection: Checking the alignment and stability of the tacked assembly before final welding.
Essential Skills for Tack Welding
Tack welding requires a specific set of skills and attributes:
- Attention to Detail: Precision is crucial in aligning workpieces and applying tack welds.
- Manual Dexterity: Steady hands and good hand-eye coordination are essential.
- Blueprint Reading: Understanding technical drawings and specifications.
- Basic Welding Knowledge: Familiarity with various welding techniques and equipment.
Equipment Needed for Tack Welding
Tack welders use a range of tools and equipment to perform their tasks effectively:
- Welding Machine: MIG, TIG, or Stick welding machines are commonly used for tack welding.
- Welding Helmet and Gloves: Personal protective equipment (PPE) to ensure safety.
- Clamps and Fixtures: To hold the workpieces in place during alignment and tack welding.
- Measuring Tools: Calipers, rulers, and squares for precise alignment.
Tack Welding Techniques
There are several techniques used in tack welding, depending on the materials and the final welding process:
MIG (Metal Inert Gas) Tack Welding
- Fast and Efficient: MIG welding is popular for tack welding due to its speed and ease of use.
- Suitable for Thin Materials: Ideal for thin sheets and light structures.
TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) Tack Welding
- Precision Welding: TIG welding offers high precision, making it suitable for intricate and delicate workpieces.
- Clean Welds: Produces clean and neat tack welds with minimal spatter.
Stick (Shielded Metal Arc) Tack Welding
- Versatile: Suitable for a wide range of materials and thicknesses.
- Robust Welds: Creates strong tack welds, ideal for heavy-duty applications.
Best Practices for Tack Welding
To ensure high-quality tack welds, follow these best practices:
- Clean Surfaces: Remove any dirt, rust, or oil from the workpieces before welding.
- Use Proper Settings: Adjust the welding machine settings according to the material and thickness.
- Apply Small Tack Welds: Keep tack welds small to minimize distortion and make them easy to remove if necessary.
- Consistent Spacing: Space the tack welds evenly to ensure uniform stability.
Conclusion
Tack welding is a fundamental step in the welding process, crucial for achieving precise and stable final welds. Tack welders play a vital role in various industries, ensuring that workpieces are accurately aligned and securely held in place. By understanding the techniques, skills, and equipment involved in tack welding, aspiring welders can master this essential skill and contribute to high-quality welding projects.
Whether you’re starting your welding career or looking to enhance your skills, mastering tack welding is a valuable asset that will set you apart in the field. Embrace the precision and attention to detail required for tack welding, and you’ll be well on your way to becoming a skilled and sought-after welder.

James is a welding expert, accomplished author, and trusted guide with over 8 years of experience in the industry. With his in-depth knowledge and engaging writing style, James has become a true authority in the field, offering readers and clients invaluable expertise and insights to take their welding skills to new heights.