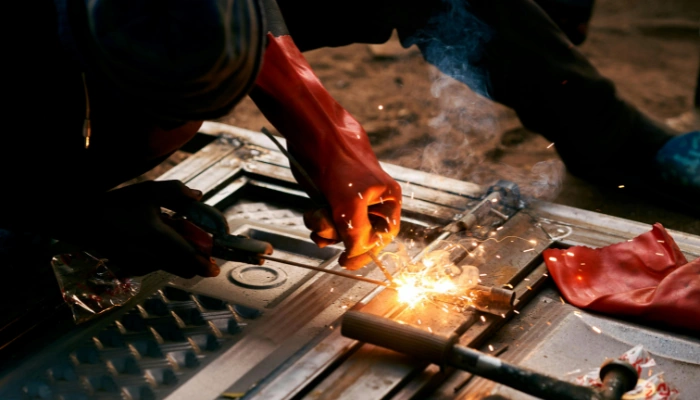
Grounding of a welding machine is one of the most important safety steps in any welding setup. Whether you are working in a home garage, professional workshop, or industrial site, understanding how to properly ground a welding machine safely protects you from electric shock, prevents equipment damage, and ensures stable welding performance.
Many beginners confuse the work clamp with true electrical grounding. While they are related, they serve different purposes. Improper grounding can cause unstable arcs, overheating, electrical hazards, and even fire risks. In this complete guide, you’ll learn exactly what grounding means, why it matters, and how to do it correctly.
Table of Contents
What Does Grounding a Welding Machine Mean
Grounding in welding refers to creating a safe electrical path that directs unwanted electrical current into the earth. This prevents dangerous voltage buildup on metal parts and reduces the risk of shock.
There are two commonly misunderstood concepts:
Work Clamp (Welding Ground Clamp)
The work clamp connects the welding machine to the metal workpiece. It completes the electrical circuit required for welding. This is not the same as earth grounding.
Earth Ground (Protective Grounding)
Earth grounding connects the welding machine frame to the ground using a grounding rod or building electrical grounding system. This protects the operator from electrical faults.
Both are important, but only proper earth grounding protects against electrical shock from internal faults.
Tools and Materials Needed for Proper Grounding
Before grounding your welding machine, gather the following:
- Copper grounding wire (appropriate gauge)
- Ground rod (usually copper or copper-coated steel)
- Ground clamp
- Hammer or ground rod driver
- Multimeter
- Protective gloves
- Safety glasses
Using quality materials ensures safe and long-lasting grounding.
Why Grounding a Welding Machine Is Essential
Grounding is the process of creating a direct physical connection between the welding machine and the earth. This connection provides a path for electrical current to safely dissipate in the event of a fault or malfunction. Here’s why grounding is so critical:
1. Safety
Grounding reduces the risk of electrical shock to the operator and others in the vicinity. If a fault occurs, such as a short circuit or insulation failure, the electrical current will flow to the ground rather than through the operator’s body, minimizing the risk of injury or fatality.
2. Equipment Protection
Proper grounding helps protect the welding machine and other electrical equipment from damage caused by electrical surges or faults. Grounding prevents electrical overloads, which can result in expensive repairs or replacements.
3. Compliance with Regulations
Grounding is often a legal requirement and part of electrical safety standards. Ensuring your welding machine is properly grounded helps you stay compliant with local and international safety regulations.
4. Improved Welding Performance
Grounding can improve the stability of the welding arc, leading to better weld quality. A stable arc is less likely to fluctuate, reducing spatter and ensuring a cleaner, more precise weld.
How Grounding of a Welding Machine Works
The grounding process involves connecting the welding machine’s ground terminal to the earth or a suitable grounding point. This connection provides a safe path for any stray electrical current to follow. Here’s how it works:
1. Ground Clamp
The ground clamp is attached to the workpiece or a metal surface close to the welding area. This clamp is connected to the welding machine by a grounding cable. The clamp ensures that the workpiece is at the same electrical potential as the welding machine, allowing the current to flow smoothly during welding.
2. Grounding Electrode
The grounding electrode, often a metal rod driven into the ground, serves as the actual point of contact with the earth. The welding machine is connected to this electrode via a grounding wire. This connection provides a direct path for electrical current to dissipate into the earth in the event of a fault.
3. Grounding Wire
The grounding wire is a critical component that connects the welding machine to the grounding electrode. This wire must be of appropriate gauge and material to handle the potential electrical current. Copper is commonly used for its excellent conductivity and durability.
4. Bonding
Bonding involves connecting all the metal parts of the welding machine and the work area to the same grounding system. This ensures that no dangerous voltage difference exists between different parts of the equipment, further enhancing safety.
Steps for Proper Grounding of a Welding Machine
To ensure your welding machine is properly grounded, follow these steps:
1. Check Local Regulations
Before setting up your grounding system, review local and national electrical codes to understand the specific requirements for grounding welding machines. Compliance with these regulations is mandatory and critical for safety.
2. Inspect the Ground Clamp
Ensure that the ground clamp is in good condition and free from corrosion or damage. The clamp should have a strong grip on the workpiece to maintain a solid electrical connection.
3. Select the Appropriate Grounding Electrode
Choose a grounding electrode that meets the requirements for your specific setup. The electrode should be driven into the ground to a depth that ensures a good connection with the earth, typically around 8 feet deep for most applications.
4. Use the Correct Grounding Wire
Select a grounding wire that is appropriate for the welding machine’s amperage and voltage. The wire should be securely connected to both the welding machine and the grounding electrode.
5. Bond All Metal Parts
Ensure all metal parts of the welding machine, including the frame, enclosure, and any metal structures in the work area, are bonded to the same grounding system. This helps eliminate the risk of voltage differences that could lead to shock or equipment damage.
6. Test the Ground Connection
Before starting any welding operation, test the ground connection to ensure it is functioning correctly. Use a multimeter or a specialized ground tester to check the continuity and resistance of the grounding system. The resistance should be as low as possible, ideally less than 1 ohm.
Where to Connect the Ground Clamp on a Welding Machine
Many welders ask where exactly to attach the ground clamp.
The best location:
- Directly on the workpiece
- On clean, unpainted metal
- As close as possible to the weld zone
Avoid attaching the clamp:
- To painted surfaces
- To rusted metal
- To distant structural steel
- To unstable or moving objects
Proper placement improves arc stability and reduces resistance.
How to Test Welding Machine Grounding
Testing is essential for safety.
Using a Multimeter
- Set the multimeter to resistance mode.
- Place one probe on the welding machine frame.
- Place the other probe on the ground rod.
- Check resistance reading.
Low resistance indicates good grounding.
Visual Inspection
- Look for corrosion
- Check tightness of bolts
- Inspect cable insulation
Testing regularly ensures long-term safety.
Common Grounding Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
1. Using Inadequate Grounding Electrodes
A common mistake is using grounding electrodes that are too short or made from improper materials. Always use electrodes that meet the necessary specifications for your welding setup.
2. Improper Ground Clamp Placement
Placing the ground clamp too far from the welding area or on a dirty or painted surface can lead to poor grounding. Ensure the clamp is placed on a clean, bare metal surface close to the weld.
3. Neglecting Regular Inspections
Failing to regularly inspect the grounding system can lead to unnoticed faults or corrosion, compromising safety. Regularly check the condition of the ground clamp, wire, and electrode to ensure they are in good working order.
4. Using Improper Grounding Wires
Using a grounding wire that is too thin or made from a low-conductivity material can result in overheating and potential failure. Always use wires that are rated for the specific current and voltage of your welding machine.
FAQs How to Properly Ground a Welding Machine Safely
Does a welding machine need to be grounded
Yes, grounding protects against electrical faults and reduces shock risk.
Is the welding ground clamp the same as earth ground
No, the work clamp completes the welding circuit, while earth grounding protects the operator from electrical hazards.
How far should the ground clamp be from the weld
Place it as close as possible to ensure stable current flow and reduce resistance.
Can improper grounding damage a welder
Yes, especially inverter welders with sensitive electronics.
How often should I check grounding connections
Inspect before each welding session and test periodically with a multimeter.
Conclusion
Grounding a welding machine is a critical safety measure that cannot be overlooked. By ensuring proper grounding, you protect yourself, your equipment, and others in the work area from the dangers of electrical faults. Following the steps outlined in this guide will help you set up a reliable grounding system that meets safety standards and enhances your welding performance.
Remember, proper grounding is not just a one-time task, it requires regular maintenance and inspection to ensure continued safety and efficiency. Whether you’re a professional welder or a hobbyist, taking the time to ground your welding machine correctly is an investment in your safety and the quality of your work.

James is a welding expert, accomplished author, and trusted guide with over 8 years of experience in the industry. With his in-depth knowledge and engaging writing style, James has become a true authority in the field, offering readers and clients invaluable expertise and insights to take their welding skills to new heights.